Content organization
Page bundles
Hugo 0.32 announced page-relative images and other resources packaged into Page Bundles.
These terms are connected, and you also need to read about Page Resources and Image Processing to get the full picture.
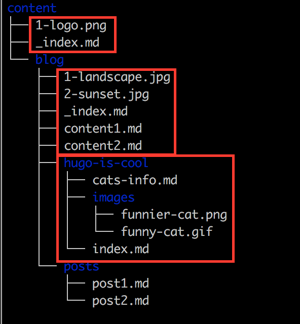
Organization of content source
In Hugo, your content should be organized in a manner that reflects the rendered website.
While Hugo supports content nested at any level, the top levels (i.e. content/<DIRECTORIES>) are special in Hugo and are considered the content type used to determine layouts etc. To read more about sections, including how to nest them, see sections.
Without any additional configuration, the following will automatically work:
.
└── content
└── about
| └── index.md // <- https://example.org/about/
├── posts
| ├── firstpost.md // <- https://example.org/posts/firstpost/
| ├── happy
| | └── ness.md // <- https://example.org/posts/happy/ness/
| └── secondpost.md // <- https://example.org/posts/secondpost/
└── quote
├── first.md // <- https://example.org/quote/first/
└── second.md // <- https://example.org/quote/second/
Path breakdown in Hugo
The following demonstrates the relationships between your content organization and the output URL structure for your Hugo website when it renders. These examples assume you are using pretty URLs, which is the default behavior for Hugo. The examples also assume a key-value of baseURL = "https://example.org" in your site’s configuration file.
Index pages: _index.md
_index.md has a special role in Hugo. It allows you to add front matter and content to your list templates. These templates include those for section templates, taxonomy templates, taxonomy terms templates, and your homepage template.
You can create one _index.md for your homepage and one in each of your content sections, taxonomies, and taxonomy terms. The following shows typical placement of an _index.md that would contain content and front matter for a posts section list page on a Hugo website:
. url
. ⊢--^-⊣
. path slug
. ⊢--^-⊣⊢---^---⊣
. filepath
. ⊢------^------⊣
content/posts/_index.md
At build, this will output to the following destination with the associated values:
url ("/posts/")
⊢-^-⊣
baseurl section ("posts")
⊢--------^---------⊣⊢-^-⊣
permalink
⊢----------^-------------⊣
https://example.org/posts/index.html
The sections can be nested as deeply as you want. The important thing to understand is that to make the section tree fully navigational, at least the lower-most section must include a content file. (i.e. _index.md).
Single pages in sections
Single content files in each of your sections will be rendered as single page templates. Here is an example of a single post within posts:
path ("posts/my-first-hugo-post.md")
. ⊢-----------^------------⊣
. section slug
. ⊢-^-⊣⊢--------^----------⊣
content/posts/my-first-hugo-post.md
When Hugo builds your site, the content will be output to the following destination:
url ("/posts/my-first-hugo-post/")
⊢------------^----------⊣
baseurl section slug
⊢--------^--------⊣⊢-^--⊣⊢-------^---------⊣
permalink
⊢--------------------^---------------------⊣
https://example.org/posts/my-first-hugo-post/index.html
Paths explained
The following concepts provide more insight into the relationship between your project’s organization and the default Hugo behavior when building output for the website.
section
A default content type is determined by the section in which a content item is stored. section is determined by the location within the project’s content directory. section cannot be specified or overridden in front matter.
slug
The slug is the last segment of the URL path, defined by the file name and optionally overridden by a slug value in front matter. See URL Management for details.
path
A content’s path is determined by the section’s path to the file. The file path
- is based on the path to the content’s location AND
- does not include the slug
url
The url is the entire URL path, defined by the file path and optionally overridden by a url value in front matter. See URL Management for details.